Building enterprise software has never been easier thanks to advances in cloud Low-Code, No-Code, and Codeless aPaaS applications platforms.

Data Fabric: What Is It and Why Every Business Needs One
What is a Data Fabric?
…And Why Do You Need One?
Written by Ian C. Tomlin | 12th January 2024
Heard about data fabrics, data lakes and data mesh solutions? Wondering what all the fuss is about? Find out here.
Data access, the innovation imperative
24/7 eCommerce means that every business faces stiff competition from competitors located around the world. Brand experience has become the primary competitive weapon. It means every business needs to be digital with decisions based on data, not conjecture. Companies that don’t harness data and modern innovations like artificial intelligence, blockchain, bots, and 3D visualization, etc. face extinction.
Why do you need a data fabric?
The organization and exploitation of business data are central to the effectiveness of any business seeking to thrive in the digital era. Before data can be fully harnessed, it needs to be harvested and blended into a common structural design, where every table and row has its place. This ‘layer’ of composable data is also known as a Data Fabric. A data fabric is the foundation stone to achieve digital ambitions. It is the key to implementing digital transformation at scale–and specifically to the edge of the enterprise, where it is arguably most needed.
Unbundling data from data silos and disparate data sources
Data is commonly managed and stored by the IT systems that produce it. In a modern IT enterprise architecture, businesses will use a variety of SaaS apps, in addition to Cloud-Native applications, and platforms, like Google, Amazon, Office365, Facebook, LinkedIn, etc. It means that data is fragmented across data silos, making it all but impossible for business users to access data when they need it. The rising authority of departmental leaders to make their own IT decisions over the past decade has only served to increase data complexity, adding to the challenges of IT and Data Security leaders charged with protecting and leveraging data. In most organizations, business systems and data systems are the same thing.
The need to re-think data management
Enterprise data delivery is broken; workers today lack access to the data they need to do their jobs, while executives lack insights to answer what-if questions and make data-driven decisions. For data engineers, the first problem in any new project is to bring data together from its current source, cleanse, de-dupe, and normalize it, etc. before any serious work can begin to answer new questions, solve problems and build apps. In most cases, spreadsheets become the only accessible tool to organize data into a useful format. Meanwhile, data governance capabilities remain woefully poor. This has led to boardroom discussions on digital transformation to pivot towards data access, data sharing, and how to decouple data from the data silos to make it more reusable. Improving data consumption and data quality are now business-critical issues.
Fragmented data architectures slows down the time-to-value delivery of new projects.
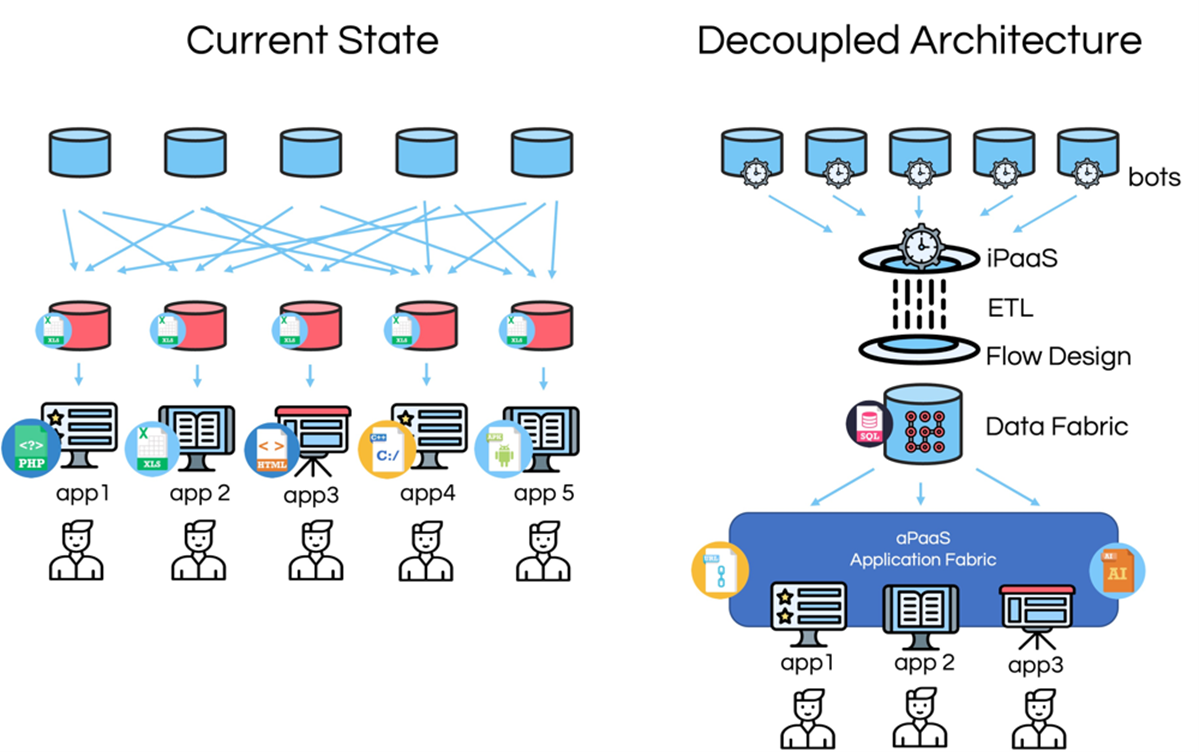
Data fabric: what it is and what it looks like
A data fabric is a conceptual data layer that spans your enterprise, releasing data from the applications and systems where data assets are found, to pre-process and organize it in such a way that it can be made useful for composing reports and be consumed by applications to facilitate machine-to-machine automation.
A data fabric solution creates a unifying data umbrella layer across your enterprise. It means data is presented in a ready-to-use format. Its main elements include:
1. Data Integration Tools to connect existing systems that hold data to the data ecosystem.
2. Extract, Transform and Load Technology to harvest and integrate with data sources, with added tools to design Master Data repositories.
3. Data Mashup Technology to pluck data from existing data sources into new structures and enrich with new data structures to meet new data demands.
4. Monitoring, Validation, and Data Integrity Tooling to ensure that data pipelines are working correctly to present data from endpoints while preventing corrupted or high-risk data from being accepted into the data fabric.
5. Analytical Tooling and Applications Development Software to consume data and present it for different uses.
A data fabric enables a new standard in data management, presenting data of high integrity that data scientists can use to automate processes and answer questions.

DIGITAL DOCUMENTS REMASTERED
Micro-Portals • Forms • Reports • Training Dashboards • Charts • Maps • Tables Checklists • Onboarding • Risk Registers • Presentations • eBooks
Data Vault, Data Fabric, Data Lake, or Data Mesh—what’s the difference?
The terminology used in the data industry can be confusing. Here we try to unbundle the terms commonly used in data architectural discussions.
Data Vault
You create a Data Vault by designing a data taxonomy around core business intelligence ‘landscapes’ and the core data tables used to describe them. Typically, these are the core records that identify your customers, suppliers, risks, opportunities, projects, products, etc. This creates a structured model of your critical data assets. Then, data is normally ‘poured in’ to this by uploading it from its host system and transforming it into a unified single version of the truth. Data Vaults are typically created using either relational databases or flat-file ‘big data’ systems.
Data Lake
A data lake is a centralized repository built to store, process, and secure large amounts of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, storing data in its native format. It is a very specific technological construct that relies on cloud computing and big data technologies to manage vast amounts of aggregated data, organized into a pre-planned taxonomy. Back in the day, people would talk about data warehouses when thinking about a centralized repository, but cloud computing has changed the narrative. Whilst Data Lake technology is extremely powerful, it isn’t always practical or affordable.
Data Fabric
A data fabric is less about an IT platform (as per a data lake) and more about an outcome: it describes the data mart layer used to make data valuable to the enterprise autonomous and composable. Your data fabric will contain business logic rules that dictate how data is shared, used, managed and consumed.
Data Mesh
A data mesh is more about philosophy and the recognition that businesses have previously seen value in owning data (and thereby trying to control and manage it internally to their business), whereas now, it’s increasingly recognized that harnessing third-party data and sharing it can yield more data asset value. A data mesh exists therefore within, across, and beyond the enterprise as a federated data ecosystem.
What are the benefits of a data fabric architecture?
Strategic ambitions
A key strategic element of a data fabric architecture is the separation of the data layer from the application layer, fostering greater re-usability of both. Businesses looking to adopt a data fabric approach site one or more of the following objectives. To:
- Liberate data from old, inflexible legacy core systems
- Transfer the ownership of data from IT to the business
- Bring data transparency to create a curious, learn fast/fail fast, data-driven decisioning culture
- Speed time to value of new projects and digital services
Overcoming spreadsheet overload
Overcoming the risks associated with the use of spreadsheets has become a widescale priority because of data security and privacy compliance. When data is used in spreadsheets, it becomes largely ‘invisible’ to those responsible for data governance.
Additionally, spreadsheets are costly to produce and manage because of the manpower overheads used to drive them.
Furthermore, spreadsheet files are prone to corruption and often contain formulas that only the creator understands, creating a single point of failure.
For all these reasons, industrializing information management by replacing spreadsheets with a robust and resilient data fabric architecture makes sense.
Hyperautomation and digital transformation
For organizations determined to reduce headcount and drive down back-office costs, removing the human in the loop is a prime driver for data fabrics.
Becoming data driven
While the importance of liberating data from data silos, spreadsheets, and increasing the pace of innovation are all good reasons for a data fabric architecture, there’s no question that most organizations will adopt it because it’s the only way for an enterprise to become truly data driven.
Case stories and examples
Ask anyone whether they feel well served by data and they will probably have their own horror story of having to use spreadsheets to harvest and manually crunch data to answer a question or solve a problem. Others will be using a spreadsheet as a quasi-business application because their IT team is too busy to find a robust alternative.
While the ambition to create a data fabric that spans the enterprise is a desirable one, getting to it can be costly. There will always be a need to achieve quick wins along the way. It’s likely that early-stage solutions will be solving problems at a departmental or functional level.
In this section, we’ve pulled together some examples of how data fabric architectures are being used to solve business problems. Applications for decoupling span the enterprise, although justifications for projects can originate at a departmental level, as illustrated by the examples below.
Managing growth performance across a sales territory
The sales division of a global electronics company responsible for the Middle Eastern, Eastern Europe, and African markets was being hampered by a shortfall in sales insights as the result of its widespread data silos. This meant the data-gathering process was time and effort intense.
Managers were presented with copious data but no actionable insights or recommendations for action. To resolve it, a data fabric was created across the regional sales platforms and ERP data repositories that could deliver timely actionable insights to stakeholders on demand. Read the full case story.
Creating a Customer Data Platform (CDP) to focus operations toward profitable business
The management team of a progressive Office Equipment and technology business in Europe identified the need to become ‘data driven. The sales leadership wanted to create a single view of its customers to focus sales efforts on the most profitable opportunities and automate delivery processes. Read the full case story here.
Scanning the market horizon, and matching resources to opportunities
Power and Energy is a fast-changing market. In the professional services industry, becoming adept at surfacing new advisory opportunities–also knowing what advisory services to offer and how to resource them–is critical to success. Find out how one global advisory firm used a decoupling architecture to gain a competitive advantage.
Why codeless PaaS technology is critical to forming a data fabric
Codeless Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) solutions take many forms. In the case of Encanvas, its codeless PaaS includes integration and application layers.
Integration, software bots, and Extract, Transform and Load (ETL) componentry bring data together in a data fabric.
Then, codeless software is used to design, publish and manage composed applications and machine-to-machine automations.
Removing the need to program system interfaces, specify information flows using scripts, and write code (or script) to create, publish and manage apps substantially cuts the time and effort needed to implement an effective data fabric and application fabric: the two building blocks of a modern Composable Data Architecture.
Missing building blocks of enterprise data management
When organizational priorities for IT are dictated by departmental managers seeking to address operational challenges with point-specific solutions, this inevitably leads to more data silos and a whole series of missing pieces in data architectures.
One of these is the vital framework of data bridges that link data elements together. It’s not uncommon, for example, to find an enterprise resource planning and customer relationship management solution using different fields to identify a customer. Equally, financial systems may not be correctly configured to identify product or service line profitability. When such data relationships are absent, it’s not possible to ask ‘what-if’ questions that combine multiple data sources, without first bringing data together into a new structure.
Another missed opportunity is the ability of an enterprise to understand its digital DNA. This is the data that helps an organization define itself, such as the organizational structures, locations, people, processes, suppliers, systems, risks, and data elements that define an organization’s makeup and capability.
For digital transformation to work you need data fabric architectures
Businesspeople have been waiting for the day when they could ask what-if questions and access the data they need to do their jobs more efficiently. Businesses want to be data-driven, implement automation at scale, tie front-end and back-end systems together to serve customers better, and bring transparency to data processing. All these ambitions rely on access to useful data. Consequently, conversations around data services have moved beyond slow-to-build data warehouses and crude point-specific solutions powered by spreadsheets. Enterprise IT has become less about systems and more about data asset value and reuse. The good news is that codeless PaaS technology makes the implementation of a data fabric affordable as it takes far less time and effort to overcome the issue of data siloes.
Delivering a stand-out customer experience dictates the need for data virtualization
In most digital industries, competitiveness comes down to customer experience. To achieve simpler customer journeys, more self-service, faster turn-arounds on orders and requests, to adapt faster to market needs, etc., all these outcomes rely on having faster access to more useful data. Achieving data virtualization by releasing data from systems that hold it to ransom through the formation of a data fabric holds this promise.
Data Lakes are not the answer to every problem
Whilst the technology is certainly catching the headlines, it would be wrong to assume that harvesting everything into a data lake is a complete or fool proof solution. There are many wheels to the data fabric wagon and getting data into a single ‘place’ may be a misguided outcome priority for some organizations. Sometimes, there are quicker wins to be gained by delivering data fabrics across departments and solving a handful of high-priority projects.

DIGITAL DOCUMENTS REMASTERED
Micro-Portals • Forms • Reports • Training Dashboards • Charts • Maps • Tables Checklists • Onboarding • Risk Registers • Presentations • eBooks
Related content
Building enterprise software
Deliver small and wide data with digital documents
How digital documents deliver small and wide data, allowing data-driven enterprises to optimize their business models and efficiency,
Digital Data Fabric
In this article, find out about our enterprise digital data fabric platform, what it is and why your business needs one.