EXPERIENCE ENCANVAS IN 60-MINUTES!
We're always happy to walk you through Encanvas no matter where you are in the world.
According to Wikipedia ‘software development’ is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components. It’s a reasonable description. At Encanvas, because we use no-lo software development tools and methods, the need to program or de-bug becomes irrelevant. We therefore describe it as – ‘The process of scoping, designing, deploying, documenting, testing, and tuning software applications.’
Over the years there have been several popular methods of developing software. These are articulated by the lifecycle a development takes from initial conception to completion, and beyond. We summarise these here.
As the term suggests, with waterfall development, a series of software developers (normally using different tools) are tasked with performing blocks of development. These activities are supervised by a project leader who sets out the development plan. Often, developers will disappear for days until the next project review meeting. This approach used to be the most common, particularly when the need to use different tools (demanding the skills of different developers) meant there was no other way.
The existence of more versatile cloud software development environments has made it possible for agile software development to happen. The underpinned principle of agile development is that small teams, meeting regularly (in a scrum), agreeing what needs to be done, sprinting to get them produced in a day, then reviewing progress speeds up software development considerably. Unfortunately, this step forward in the software development approach does little to eradicate the project overheads and risks associated with manual coding.
Use of codeless (requires developers to no longer see or use code) Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) has made it possible for software developments to be managed by one person from start to end. The key design role is performed normally by someone with business analyst skills, as appreciating what needs to be created – and why – becomes the greater risk to project failure. This has led to the ability of software development to happen in workshops, in near-real-time. At the term suggests, live wireframing focuses on rapidly developing a live wireframe ‘prototype’ of a solution and ‘failing fast.’ Through the use of an integrated development environment, it’s possible to de-risk projects by iterating designs at a very low cost.
Software development is known to be a hugely wasteful process.
A Harvard Business Review article article ‘Why Your IT Project May Be Riskier Than You Think’ published in November 2011 uncovered that, followed a survey of 1,471 IT projects with an average spend of $167m:
This level of performance has changed little in the intervening period. So, why are software development projects so inconsistent in their delivery? There are a number of factors:
Specifying how an application should work – the process it must fulfill, the aspirational needs of stakeholders, user interface, the logic rules, data integration, and processing, etc. – is complex. Working with stakeholders unsure of what they need, and struggling to visualize how it will work for them, makes it even more difficult.
Calculating a Return-on-Investment It’s hard to envision ‘how well’ a software development will work, and the level of influence the application will have in improving the process.
When multiple individuals are working on the same project using different software development tools, it’s difficult to keep everyone on the same page and keep developments on-track. Even when projects manage this, the consequence of using a blend of development tools means that a small change to one aspect of development can have a big knock-on effect. For example, changes to the database structure can demand changes to front-end forms, requests for reports can expose shortcomings in data designs, etc.
Anyone that’s ever tried their hand at coding or scripting knows that it’s a slow and detailed process. When code is created manually, there’s always the risk that errors will be made. Worse still, there is a risk of malware being introduced or intellectual property loss. These risks demand that applications are heavily tested before they are released. This costs a lot of time and money to do. Any changes result in a new wave of developments.
It’s not uncommon for users and stakeholders of a software development to change their minds over what’s needed. When this happens, it can significantly delay or even de-rail developments.
Few applications function in isolation. Normally they need to take data from third-party systems or deposit it somewhere. The quality of data and the challenges of integration can take 30 to 45 percent of the project-spend. When data is poor, the RoI of projects can reduce or be completely removed. Data quality can make software developments redundant.
When an application is used by a community of users or customers and they request changes to be made over time, this can result in development teams to have to support more than one version of their software. Unless some pre-planning goes into how platform versioning is managed, it can result in a long tail of code management overheads.
Encanvas is an enterprise software company that specializes in helping businesses to create above and beyond customer experiences.
From Low Code to Codeless
Better than code-lite and low-code, we created the first no code (codeless) enteprise application platform to release creative minds from the torture of having to code or script applications.
Use Encanvas in your software development lifecycle to remove the barrier between IT and the business. Coding and scripting is the biggest reason why software development has been traditionally unpredictable, costly and unable to produce best-fit software results. Encanvas uniquely automates coding and scripting. Our live wireframing approach means that business analysts can create the apps you need in workshops, working across the desk with users and stakeholders.
When it comes to creating apps to create a data culture and orchestrate your business model, there’s no simpler way to instal and operate your enterprise software platform than AppFabric. Every application you create on AppFabric adds yet more data to your single-version-of-the-truth data insights. That’s because, we’ve designed AppFabric to create awesome enterprise apps that use a common data management substrate, so you can architect and implement an enterprise master data management plan.
Encanvas supplies a private-cloud Customer Data Platform that equips businesses with the means to harvest their customer and commercial data from all sources, cleanse and organize it, and provide tooling to leverage its fullest value in a secure, regulated way. We provide a retrofittable solution that bridges across existing data repositories and cleanses and organizes data to present a useful data source. Then it goes on to make data available 24×7 in a regulated way to authorized internal stakeholders and third parties to ensure adherence to data protection and FCA regulatory standards.
Encanvas Secure and Live (‘Secure&Live’) is a High-Productivity application Platform-as-a-Service. It’s an enterprise applications software platform that equips businesses with the tools they need to design, deploy applications at low cost. It achieves this by removing coding and scripting tasks and the overheads of programming applications. Unlike its rivals, Encanvas Secure&Live is completely codeless (not just Low-Code), so it removes the barriers between IT and the business. Today, you just need to know that it’s the fastest (and safest) way to design, deploy and operate enterprise applications.
Learn more by visiting www.encanvas.com.
Mason Alexander is a senior consultant specializing in helping organizational leadership teams to grow by implementing enterprise software platforms that improve data visibility, process agility; and organizational learning – creating an enterprise that learns and adapts faster. He writes on subjects of change management, organizational design, rapid development applications software, and data science. He can be contacted via his LinkedIn profile.

Data management (DM) consists of the practices, architectural techniques, and tools for achieving consistent access to and delivery of data across the spectrum of data subject areas and data structure types in the enterprise, to meet the data consumption requirements of all applications and business processes.
Times gone by, data management was not something that business leaders needed to think about: it was built into the applications they purchased as an integral duty of the software vendor to determine how data was managed and provide administration tools to govern it.
These days, organizations want to maximize the value of data across their enterprise, and that means harvesting and re-using data. To achieve that, and do it well, organizations need to create an ‘enterprise-wide’ data management approach that extends beyond any single application.
Providing access to information quickly remains a fundamental challenge to data and knowledge management professionals.
A pivotal industry study by Accenture found that:
The same study found:
A logical question for leaders, is this: ‘Is Data Management a cost of doing business, or is it an enabler for growth?’
The potential of digital technologies to engage customers in new ways, and to provide self-service portals with which to orchestrate business models, has transformed leadership perceptions of the role of data management from being an IT administrative hygiene issue, to a primary competitive advantage.
Online retailers like Amazon are demonstrating how effective data management, in their case customer data, can result in unprecedented opportunities for growth. Amazon has set as its objective the desire to deliver awesome customer experience through the deepest knowledge possible of who customers are and what they care about. They see data management as an integral part of that story.
Airlines like easyjet, have invested considerably, although astutely, on inhouse developed systems based on the Microsoft .NET / Microsoft Azure platform that data management platforms like encanvas secure&live also use. Easyjet has streamlined flyer booking and their ‘from home to the gate’ experience, to make flying more convenient for passengers, while also supersizing their customer data capture opportunities from the self-service customer portals they have created.
Retailers like Tesco have established very effective voucher programs that motivate customers to buy ‘just a little more’ every time they shop by harvesting rich data about customers from in-store and online shopping behaviors. The Tesco Clubcard system affords Tesco a competitive advantage in its market by maximizing its ability to learn about what customers want by offering small voucher-based rewards.
Car Rental company HERTZ are past masters at membership schemes that reward repeat customers with benefits that improve their customer experience. It operates not one but several membership levels to target different audiences in its customer base. These card-based membership rewards schemes help HERTZ to tailor its offers, capture knowledge of the types of customer they have in their community, and learn how to tailor rewards to incentivize repeat business.
None of these initiatives would be possible without outstanding focus on data management, sponsored by data-savvy management teams who understand the value of data to their business as the ultimate competitive weapon.
At the turn of the millennium, business leaders had the expectation they could purchase a ‘System of Record’ Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software application – like Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, or SAP R3 – and they would have everything they needed ‘in the box’ with which to run their business. Again, the presumption was Data Management would be taken care of by the software provider. That hasn’t proven to be the case.
The footprint of any ERP system these days is barely 60% (if you’re lucky) of the IT systems needed to operate a company’s complete business model. The role of IT systems has extended beyond the use of internal stakeholders.
As the case examples given above show, businesses that qualify as ‘digital leaders’ are creating digital cloud platforms and ecosystems that unilaterally service the needs of customers, suppliers, shareholders, contractors and members of staff. These solutions have to be tailored and adapted to the specific audiences, operational behaviors and outcomes of the organization; something that slow-to-change ERP systems were never designed to do.
Perceptions of the role of data management have changed as organizations have come to realize the importance of maximizing the value of data. Business leadership teams are acknowledging the importance of making data-driven decisions. To achieve that, requires not only a data-driven culture, it needs data to be organized across the enterprise.
The starting point for most organizations on their data management journey is to construct a data catalog. As the name suggests, your data catalog holds a log record of all important data assets that exist in your enterprise IT systems.
In business, a data platform is any form of implementation of a database, data-mart or data warehouse used to manage business-critical data structures. More organizations these days want to house data in an enterprise data platform that maximizes its value and the ease to which data can be governed.
For many organizations, the thrust towards above and beyond customer experiences powered by data analytics means that Customer Data Platforms are becoming the first step towards enterprise data management.
A Customer Data Platform is an enterprise computer processing platform used to harvest, aggregate, cleanse, manage, process, analyze and output customer associated data. Data is pulled from multiple sources, cleaned and combined to create a single customer profile. This structured data is then made available to other marketing systems. Unlike a Customer Database, a Customer Data Platform extends its functionality to all aspects of the customer lifecycle. Normally it will include campaign management and the provisioning of multi-channel communications. Advanced systems will manage customer offers and promotions.
The CDP Institute defines a Customer Data Platform as “packaged software that creates a persistent, unified customer database that is accessible to other systems.” Basically it’s a prebuilt system that centralizes customer data from all sources and then makes this data available to other systems for marketing campaigns, customer service and all customer experience initiatives. Gartner defines CDPs as – ‘integrated customer databases managed by marketers that unify a company’s customer data from marketing, sales and service channels to enable customer modelling and drive customer experience.’ At encanvas, we see this as a narrow definition, given that Customer Data Platforms normally serve up insights to strategic teams and all departmental functions to shape processes and priorities.
This raises the challenges of ‘who owns the problem.’ Often, IT leaders are too busy concentrating on core IT systems and ‘keeping the lights on’ to then deal with data management and governance issues too.
Although tooling to enable data management technology has matured beyond recognition over the past decade, the fundamental challenge facing all organizations remains to be data quality issues. As organizations engage in projects to build an enterprise-wide view of data, and commence to task of harvesting data from operational systems, it becomes apparent how poorly business software applications manage the integrity of data they hold. These integrity issues happen for three main reasons:
Always the run-up to data quality on lists of data management challenges, are the data management challenges brought about by the existence of systems and organizational silos.
Over time, businesses will evolve their organizational designs and data structures, normally one department and one system at a time. They become a collection of departments rather than one homogeneous enterprise data engine. Each will run systems to satisfy department data processing needs. Managing data from across the enterprise immediately exposes the challenge that systems were never designed to work together or share data. Important data identifiers that help data scientists to forge links between disparate databases – the gateways and bridges to data – may not exist, making the task of forming a single view of data extremely difficult.
Industry practitioners agree that the three key steps to achieving effective enterprise data management are themselves not complicated. They are to:
Although these steps seem trivial and obvious, it is a path paved with difficulties and a track-record of poor success. The list of failed projects includes some of the world’s largest companies and brands you might think should know better, or at least could afford to fix the issues they encountered along the way.
Whatever the size and scale of the data management project, it requires very clear and measurable reasons for doing it, and unrelenting management commitment. The reality is, that it will inevitably take longer and cost more than project leaders would like.
There are lots of good reasons why organizations should put a focus on organizing their data. We describe the top ones here.
Departmental managers and knowledge workers continue to complain about difficulties in accessing the data they need to discharge their roles. Searching for data that may or may not exist can feel like a huge waste of time for busy workers. Knowing where to look for data is normally a good start to improving accessibility to data. Tools like knowledge portals and Wikis can make a big difference to the ability of workers to find answers and content resources. Having ONE PLACE where knowledge is held offers the best starting point for organizations that today use multiple instances of content management and knowledge sharing systems. Social tools have the potential to change organizations, but only if those tools are implemented in a way that changes how individual employees work day to day.
Executive teams that are unable to harvest data insights to answer their strategic questions have no other choice but to work off of hunches and gut-feel. Taking reports and insights from discreet operational systems creates a kaleidoscope view of operational realities. Executives team reliant on silo-reported data-sets claim to find it hard to gain a consistent impression of organizational performance and struggle to answer strategic questions. The cost of acquiring answers to strategic questions is extremely high, to the point of making it uneconomic.
Without some form of enterprise data warehouse, re-using data and harvesting its value becomes extremely difficult, if not impossible.
Having the ability to holistically understand your customers, systems, assets, products, supply-chain, partner channels, etc. makes a big difference to the ability of the enterprise to respond to change, opportunity and risk as it emerges. To achieve this, key data-sets need to be carefully structured and governed.
Not knowing where data is, and who can view and edit it, is a big risk to businesses. One of the challenges of data breaches is not knowing what data has been compromised in the event of a breached. Data security professionals need to know where precious data is and how users and user groups are governed to restrict privileges according to need and risk.
The advent of the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has had a profound effect on the Data Management discipline. The risk of data loss has become a business continuity threat (fines of up to 4% of global turnover may be levied by litigators) and this has resulted in a compelling RoI argument for enterprise data management and data quality enrichment projects, perhaps for the first time.
The influence of the GDPR on Data Management doesn’t stop there. To implement data privacy safeguards, organizations are obliged to know where privacy data exists. In many organizations today, that simply isn’t possible owing to a fragmented departmental and systems view of data assets.
While organizations find it harder to justify investments based on growth potential, it is easier for financial professionals to justify spend on Data Management qualified by a measurable cost and risk implication.
When implementing an enterprise data catalog, some of the most important data is that which describes the enterprise; it’s companies, locations, organizational hierarchies, people, roles, processes, data, systems, risk and suppliers. Rarely is this information manage in a digital form in one place, if indeed it exists at all. The obstacle this presents ion data science is the lack of data context that exists without it.
Master data management is a tern used to describe methods used to holistically define and manage the critical data of an organization. The general priority of Master Data Management projects is to define a single version of the ‘data truth’ across the enterprise. Relatively few organizations have implemented robust MDM models, chiefly because of the costs involved and the absence of a clear return-on-investment. A good proportion of those organizations with effective MDM implementations have evolved their data management from the ground up, with strong executive leadership to make it happen. Retrofitting MDM across an existing enterprise IT architecture operating hundreds of applications is a non trivial and costly task.
Self-service reporting is ‘the customer’ of Data Management. Without the ability of machines and humans to harvest it, data serves little purpose.
Self-service reporting is an analytics paradigm that places the emphasis for data analysis and report-building on individual citizen users instead of highly trained statisticians or data scientists.
Advances in data visualization and business intelligence are making it progressively simpler to make sense of large data sets and to pull-out the things leaders, managers, workers and machines want to know. Technology is democratizing data analytics to bring its influence on an increasingly data aware, and data hungry enterprise. Whereas data management and analytics has been a specialist technical discipline, it’s entirely likely that a decade from now, we will see it as something every worker does.
Data science is one of the buzz-terms of the enterprise computing industry. This realization, that data is important as a competitive differentiator and that a technical competency was needed to harness it, began with the evolution of big data and cloud computing. It quickly became apparent that the combination of big data and artificial intelligence would mean a substantive increase in the pace of digital business and the need to analyze, interpret and act on unimaginably large volumes data both faster, and more often. The industry of data science was born.
The term Data Science describes the broad set of scientific methods, processes, algorithms and systems used to extract knowledge and insights from many structural and unstructured data. Data science is related to data mining and big data.
The true value and therefore effectiveness of Data Management remains compromised in organizations as the result of self-authored desktop applications that perpetuate shadow data, that exists unbeknown to IT.
Spreadsheets remain as the most prolific producer of shadow data. Use of spreadsheets means data scientists lose vital data assets because the data is held in desktop hard-drives in unusable structures.
To achieve optimal results in data management, organizations must somehow find ways to eradicate self-authored applications beyond the remit and control of IT.
Encanvas is an enterprise software company that specializes in helping businesses to create above and beyond customer experiences.
From Low Code to Codeless
Better than code-lite and low-code, we created the first no code (codeless) enterprise application platform to release creative minds from the torture of having to code or script applications.
Use Encanvas in your software development lifecycle to remove the barrier between IT and the business. Coding and scripting is the biggest reason why software development has been traditionally unpredictable, costly and unable to produce best-fit software results. Encanvas uniquely automates coding and scripting. Our live wireframing approach means that business analysts can create the apps you need in workshops, working across the desk with users and stakeholders.
When it comes to creating apps to create a data culture and orchestrate your business model, there’s no simpler way to instal and operate your enterprise software platform than AppFabric. Every application you create on AppFabric adds yet more data to your single-version-of-the-truth data insights. That’s because, we’ve designed AppFabric to create awesome enterprise apps that use a common data management substrate, so you can architect and implement an enterprise master data management plan.
Encanvas supplies a private-cloud Customer Data Platform that equips businesses with the means to harvest their customer and commercial data from all sources, cleanse and organize it, and provide tooling to leverage its fullest value in a secure, regulated way. We provide a retrofittable solution that bridges across existing data repositories and cleanses and organizes data to present a useful data source. Then it goes on to make data available 24×7 in a regulated way to authorized internal stakeholders and third parties to ensure adherence to data protection and FCA regulatory standards.
Encanvas Secure and Live (‘Secure&Live’) is a High-Productivity application Platform-as-a-Service. It’s an enterprise applications software platform that equips businesses with the tools they need to design, deploy applications at low cost. It achieves this by removing coding and scripting tasks and the overheads of programming applications. Unlike its rivals, Encanvas Secure&Live is completely codeless (not just Low-Code), so it removes the barriers between IT and the business. Today, you just need to know that it’s the fastest (and safest) way to design, deploy and operate enterprise applications.
Learn more by visiting www.encanvas.com.
Mason Alexander is a senior consultant specializing in helping organizational leadership teams to grow by implementing enterprise software platforms that improve data visibility, process agility; and organizational learning – creating an enterprise that learns and adapts faster. He writes on subjects of change management, organizational design, rapid development applications software, and data science. He can be contacted via his LinkedIn profile.

Customer data is anything that identifies a customer, or indeed any associated data that results from customer interactions including purchases, transactions, and customer service communications.
A Customer Data Platform is an enterprise computer processing platform used to harvest, aggregate, cleanse, manage, process, analyze and output customer associated data. Data is pulled from multiple sources, cleaned and combined to create a single customer profile. This structured data is then made available to other marketing systems. Unlike a Customer Database, a Customer Data Platform extends its functionality to all aspects of the customer lifecycle. Normally it will include campaign management and the provisioning of multi-channel communications. Advanced systems will manage customer offers and promotions.
The CDP Institute defines a Customer Data Platform as “packaged software that creates a persistent, unified customer database that is accessible to other systems.” Basically it’s a prebuilt system that centralizes customer data from all sources and then makes this data available to other systems for marketing campaigns, customer service and all customer experience initiatives. Gartner defines CDPs as – ‘integrated customer databases managed by marketers that unify a company’s customer data from marketing, sales and service channels to enable customer modeling and drive customer experience.’ An encanvas, we see this as a narrow definition, given that Customer Data Platforms normally serve up insights to strategic teams and all departmental functions to shape processes and priorities.
Every business understands the impact of outstanding customer experience. Think of businesses like Amazon, whose singular purpose is obsessive Customer Fanaticism; placing the customer at the heart of everything it does. Even shareholders were taken aback when its founder Jeff Bezos explained that he was prepared to forego short-term profitability in exchange for an unbeatable customer experience. And he’s proven to be correct.
Like Amazon, if you want to delight customers with personalized offers then you will need to be world-class at capturing and making sense of lots of data about the customers you serve. Modern marketing methods rely on data to drive decision making. It eliminates the guesswork of content marketing because marketers know what motivates customers and the characteristics that profile the best-fit audience for their products and services.
Without a Customer Data Platform, the ability to appreciate the value and characteristics of customer relationships is rarely that straight-forward. In practice, data is stored in silos, whether organizational or technological, and this makes it challenging for companies to deliver consistent customer experiences.
An important business driver for integration services comes from the desire of executives to harvest data from across their enterprise in order to make informed decisions. The drive towards a data-driven culture demands that systems connect to one another. The integrity of data executives review, is a major sticking point.
A survey of 442 business executives around the world by Harvard Business Review found that corporate decision makers have major concerns about access to, availability of, and the quality of internal and outside data. The result is reduced confidence in their decision-making ability.
Moreover, nearly half of the global respondents said their lack of confidence stems from a lack of information or easy access to data. The findings are puzzling given the emergence of big data techniques, the proliferation of global networks and the sheer processing power contained even in mobile devices.
One reason for the disconnect between big data and decision making, the Harvard researchers found, is that “silos of data, typically imprisoned in customer, financial, or production systems, are frequently inaccessible by individuals outside the functional group.”
In this regard:
Your customer data has huge business value because it helps to improve your ability to engage customers in conversation, on topics they care about. Then, your marketing team can use customer insights to segment markets and develop tailored offers to specific groups of customers; to deliver personalized experiences, one customer, at a time. This attention to detail (and preference) has become a ‘killer-app’ in many consumer markets where buyers have so much choice.
“Customer Data Platforms help companies solve a huge and growing problem: the need for unified, accessible customer data. Like most packaged software, a CDP reduces risk, deploys faster, costs less, and delivers a more powerful solution than custom-built alternatives…With careful planning, a CDP will provide the foundation your company needs in the years ahead to meet customer expectations for exceptional personalized experiences.” — David Raab, Customer Data Platform Institute
In most businesses today, marketing teams are awash with data. The problem is, much of the data is spread across operating systems and platforms that have no means to present a single view of the customer. Only recently have senior management teams come to recognize the strategic importance of customer data and its role in delivering a competitive advantage.
As data volumes grow, and is spread across your organization and its partner ecosystem, you lose the ability to leverage it and gain a competitive advantage. Organizations come unable to assemble unified customer data.
Data quality is a huge problem. When the currency or completeness of is poor, the usefulness of insights is tested.
It’s common for operational systems not to populate all of the tables and rows that exist in back-office systems when they don’t directly benefit the specific process they serve. This can result in many of the harvested data-sets to be incomplete, or of poor quality. In consequence, organizations are unable to apply unified customer data in delivery systems.
To create high-quality data requires data to be cleansed and graded when sourced from operational systems. This requires specialist computer tooling, often driven by artificial intelligence technologies, used to vote on the best quality sources and graduate data as it is being harvested. According to the CDP Institute, something like 43% of business-to-business companies lack the ability to extract data from source systems.
Departments all benefit from a single view of the customer, but rarely can they agree who owns it and are prepared to share data to achieve it. Projects can easily be derailed as the result of inadequate budgets, poor cooperation across organizations, and a general lack of time in marketing and technology departments to commit effort into what is essentially a change management project.
Implementing a Customer Data Platform will gather data to create a unified data-mart that presents holistic landscape views of your customers and their interactions with your business – irrespective of where the data is held. The result is that all teams across the enterprise benefit from an improved understanding of what customers care about to segment more effectively, shape customer offers in more refined ways and fine-tune processes to deliver above and beyond (and personalized) customer experiences.
According to the most recent study by the CDP Institute, the top reasons that organizations buy CDP solutions are to:
For most organizations, the ultimate test of whether a Customer Data Platform is delivering optimal outcomes lies in its ability to do three things exceedingly well:
Most organizations today structure their data within the operating departments that manage processes. This only serves to fragment customer data. A Customer Data Platform requires a rethink in the way data is managed, to ensure that all facets of the customer world are incorporated into the customer data model not limited to:
One of the challenges in putting together a Customer Data Strategy is the broad cross-section of stakeholders with a voice on what the end-game should look like. The key stakeholders will tend to be any of the following:
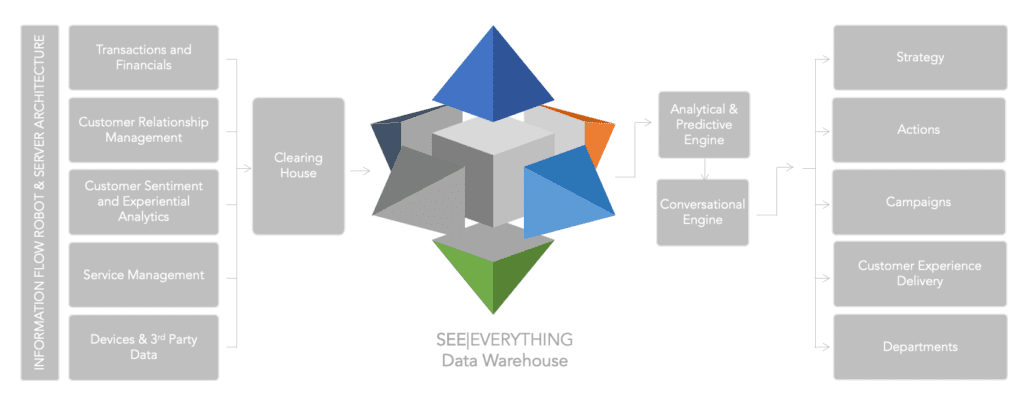
There are typically five main components of a Customer Data Platform architecture. Note, the terminology used here is formed around the Encanvas CDP but alternative solutions follow a similar path:
Here are some of the common obstacles we’ve encountered through previous projects implementing Encanvas as a Customer Data Platform:
A single view of the customer is only as effective as it is comprehensive and actionable. In the first place, the number of data sources available to a CDP is critical to the richness of insight it offers. You will want to have a comprehensive and current data set, along with the broadest platform to make use of the insights. If a Customer Data Platform has access to website data alone, then gaps will exist in the knowledge of customer interactions, transactions, etc. – and it will be impossible to accurately judge profitability. When solutions only use data to personalize a customer’s website experience, there are crucial gaps in customer experience delivery that extends beyond it – such as customer service and support.
Market analysts offer conflicting data on the size and potential of the CDP market.
Early-stage reporting from researchers at Raab Associates – attributed to having coined the category term in 2014 – made the prediction in 2017 that, after analyzing 27 CDP vendors that collectively generated more than $300 million in revenue – Customer Data Platforms (CDP) would reach $1 billion by 2019. According to a Marketsandmarkets.com survey, the customer data platform market is predicted to grow from $639.9 million in 2017 to reach $3,265.4 million by 2023 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 29.3% during the forecast period. The base year for the study is 2017 and the forecast period is 2018–2023. The customer data platform (CDP) is said to have a potential scope for growth in the years to come due to increasing adoption of the customer data platform for omni-channel customer experience and demand for real-time data availability. Researchandmarkets.com suggest major growth drivers for the market include an increasing demand for omni-channel experience and actionable insights by marketers and effective tracking of customers to understand their behavior for target marketing activities, and increasing pressure on CMOs to deliver personalized content spurring the demand for real-time data availability. Gartner, one of the generally most trusted enterprise IT analysts, have incorporated Customer Data Platforms into a broader category called Customer Experience and Relationship Management Software. They say Worldwide spending on customer experience and relationship management (CRM) software grew 15.6% to reach $48.2 billion in 2018, according to research from Gartner, Inc. CRM remains both the largest and the fastest growing enterprise application software category.
Gartner sees much of the data science aspects of Customer Data Platforms integrated within its data science and machine learning (DSML) platform category. Gartner defines a DSML platform as a core product and supporting portfolio of coherently integrated products, components, libraries and frameworks (including proprietary, partner and open source). Its primary users are data science professionals. These include expert data scientists, citizen data scientists, data engineers and machine learning (ML) engineers/specialists. Players in this space include Alteryx, Anaconda, Databricks, Dataiku, DataRobot, Domino, Google, H20.ai. IBM, KNIME, MathWorks, Microsoft, RapidMiner, SAS, TIBCO and Altair.
To define the DSML market and score vendors, Gartner has determined fifteen critical capabilities.
In addition to Encanvas, the following vendors are active in the CDP market include Oracle, SAP, Salesforce, Adobe, Nice, SAS Institute, Tealium, Segment, Zaius, AgilOne, ActionIQ, BlueConic, Ascent360, Evergage, Lytics, mParticle, NGDATA, IgnitionOne, Signal, Usermind, Amperity, Reltio, Ensighten, Fospha, and SessionM.
Encanvas is an enterprise software company that specializes in helping businesses to create above and beyond customer experiences.
From Low Code to Codeless
Better than code-lite and low-code, we created the first no-code (codeless) enterprise application platform to release creative minds from the torture of having to code or script applications.
Use Encanvas in your software development lifecycle to remove the barrier between IT and the business. Coding and scripting is the biggest reason why software development has been traditionally unpredictable, costly and unable to produce best-fit software results. Encanvas uniquely automates coding and scripting. Our live wireframing approach means that business analysts can create the apps you need in workshops, working across the desk with users and stakeholders.
When it comes to creating apps to create a data culture and orchestrate your business model, there’s no simpler way to install and operate your enterprise software platform than AppFabric. Every application you create on AppFabric adds yet more data to your single-version-of-the-truth data insights. That’s because, we’ve designed AppFabric to create awesome enterprise apps that use a common data management substrate, so you can architect and implement an enterprise master data management plan.
Encanvas supplies a private-cloud Customer Data Platform that equips businesses with the means to harvest their customer and commercial data from all sources, cleanse and organize it, and provide tooling to leverage its fullest value in a secure, regulated way. We provide a retrofittable solution that bridges across existing data repositories and cleanses and organizes data to present a useful data source. Then it goes on to make data available 24×7 in a regulated way to authorized internal stakeholders and third parties to ensure adherence to data protection and FCA regulatory standards.
Encanvas Secure and Live (‘Secure&Live’) is a High-Productivity application Platform-as-a-Service. It’s an enterprise applications software platform that equips businesses with the tools they need to design, deploy applications at low cost. It achieves this by removing coding and scripting tasks and the overheads of programming applications. Unlike its rivals, Encanvas Secure&Live is completely codeless (not just Low-Code), so it removes the barriers between IT and the business. Today, you just need to know that it’s the fastest (and safest) way to design, deploy and operate enterprise applications.
Learn more by visiting www.encanvas.com.
Mason Alexander is a senior consultant specializing in helping organizational leadership teams to grow by implementing enterprise software platforms that improve data visibility, process agility; and organizational learning – creating an enterprise that learns and adapts faster. He writes on subjects of change management, organizational design, rapid development applications software, and data science. He can be contacted via his LinkedIn profile.
Marketsandmarkets CDP market sizing research report
Prenewswire reprint of market sizing report
cmswire.com ‘Keep your eye on Customer Data Platforms’ article
CDPinstitute website offering more details about Customer Data Platforms

Change Management Software is a category of application software used to facilitate enterprise change and improvement. It helps organizations to adapt to change by anticipating needs, modifying or displacing incumbent software applications. In the context of application software development, change management involves tracking and managing changes to artifacts, such as code and requirements as part of software development life-cycle (SDLC).
Enterprise software created for Systems of Record use cases – such as Financial, Manufacturing Resource Planning, Human Capital Management, and Customer Relationship Management software – is designed to impose best practice approaches to commonly performed business-critical processes within the enterprise. It is unusual for Systems-of-Record applications to deliver a competitive advantage because they fundamentally install common blueprints and ways of working that all competitors in a market end up supporting. In contrast, change management software exists to stay in-tune with enterprise needs for information processing as business models evolve over time.
The digital age has seen a dramatic increase in the pace of change in business model designs. Whereas firms a decade ago wouldn’t change their business model more than once in a decade, today, organizations will review business model designs at least once every two years, if not more.
Change Management Software equips individuals or departments charged with business improvement – and command over the change management process within an enterprise – with the necessary tools to evolve information systems and to support the change process itself. It brings the following benefits to adopting businesses:
Since 2007, the enterprise computing industry has been progressively leveraging cloud computing technologies to make applications more accessible and available to user communities. The use of cloud hosting applications has made it possible for applications to serve markets and users 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. One of the challenges of porting applications to the cloud has been the risk of data loss. Data security has become an increasing concern to organizations because of their greater reliance on data to continue business operations. Additionally, the increased compliance risks of processing personally identifiable information (PII) have made organizations more concerned about the security risks of cloud-deployed applications. Nevertheless, most application platforms today are deployed on cloud computing platforms as an applications-Platform-as-a-Service ([aPaaS]).
Encanvas is an enterprise software company that specializes in helping businesses to create above and beyond customer experiences.
From Low Code to Codeless
Better than code-lite and low-code, we created the first no code (codeless) enterprise application platform to release creative minds from the torture of having to code or script applications.
Use Encanvas in your software development lifecycle to remove the barrier between IT and the business. Coding and scripting is the biggest reason why software development has been traditionally unpredictable, costly and unable to produce best-fit software results. Encanvas uniquely automates coding and scripting. Our live wireframing approach means that business analysts can create the apps you need in workshops, working across the desk with users and stakeholders.
When it comes to creating apps to create a data culture and orchestrate your business model, there’s no simpler way to instal and operate your enterprise software platform than AppFabric. Every application you create on AppFabric adds yet more data to your single-version-of-the-truth data insights. That’s because, we’ve designed AppFabric to create awesome enterprise apps that use a common data management substrate, so you can architect and implement an enterprise master data management plan.
Encanvas supplies a private-cloud Customer Data Platform that equips businesses with the means to harvest their customer and commercial data from all sources, cleanse and organize it, and provide tooling to leverage its fullest value in a secure, regulated way. We provide a retrofittable solution that bridges across existing data repositories and cleanses and organizes data to present a useful data source. Then it goes on to make data available 24×7 in a regulated way to authorized internal stakeholders and third parties to ensure adherence to data protection and FCA regulatory standards.
Encanvas Secure and Live (‘Secure&Live’) is a High-Productivity application Platform-as-a-Service. It’s an enterprise applications software platform that equips businesses with the tools they need to design, deploy applications at low cost. It achieves this by removing coding and scripting tasks and the overheads of programming applications. Unlike its rivals, Encanvas Secure&Live is completely codeless (not just Low-Code), so it removes the barriers between IT and the business. Today, you just need to know that it’s the fastest (and safest) way to design, deploy and operate enterprise applications.
Learn more by visiting www.encanvas.com.
Mason Alexander is a senior consultant specializing in helping organizational leadership teams to grow by implementing enterprise software platforms that improve data visibility, process agility; and organizational learning – creating an enterprise that learns and adapts faster. He writes on subjects of change management, organizational design, rapid development applications software, and data science. He can be contacted via his LinkedIn profile.

Change Management IT is a broad category of application software used to facilitate enterprise change and improvement. It helps organizations to adapt to change by anticipating needs, modifying or displacing incumbent software applications. In the context of application software development, change management involves tracking and managing changes to artefacts, such as code and requirements as part of software development life-cycle (SDLC).
At one time, an organizational change was a rare thing. Business models rarely altered and the structure of organizations – i.e. how organizational structures were designed and resourced – had no need to change. Once people were assigned roles in the organization, they rarely moved beyond their role or department. Not today. The business models organizations operate are changing frequently and rapidly.
This is because, in a digital age, the structure of markets and the nature of competition. Many new forms of competition emerge from beyond the traditional players in any given market. We are seeing retailers selling holidays, telecoms contracts and financial services products, utilities and automotive manufacturers selling data and online retailers selling everything! In such a tumultuous market for products and services, suppliers have to respond to change faster. This means organizations are facing near-constant organizational restructuring.
It’s not just people and processes, but technology too is having to adapt faster and more often to change. This means traditional IT platforms are being displaced by Low Code or Codeless enterprise software application platforms that are designed to adapt to change constantly, and offer productivity enabling tooling to serve the needs of change managers orchestrating change.
Enterprise IT created for Systems of Record use cases – such as Financial, Manufacturing Resource Planning, Human Capital Management, and Customer Relationship Management software – is designed to impose best practice approaches to commonly performed business-critical processes within the enterprise. It is unusual for Systems-of-Record applications to deliver a competitive advantage because they fundamentally install common blueprints and ways of working that all competitors in a market end up supporting. In contrast, change management software exists to stay in-tune with enterprise needs for information processing as business models evolve over time.
The digital age has seen a dramatic increase in the pace of change in business model designs. Whereas firms a decade ago wouldn’t change their business model more than once in a decade, today, organizations will review business model designs at least once every two years, if not more.
Change Management IT equips individuals or departments charged with business improvement – and command over the change management process within an enterprise – with the necessary tools to evolve information systems and to support the change process itself.
It brings the following benefits to adopting businesses:
Encanvas is an enterprise software company that specializes in Change Management IT, helping businesses to create above and beyond customer experiences.
From Low Code to Codeless
Better than code-lite and low-code, we created the first no code (codeless) enteprise application platform to release creative minds from the torture of having to code or script applicationsLive Wireframe
Use Encanvas in your software development lifecycle to remove the barrier between IT and the business. Coding and scripting is the biggest reason why software development has been traditionally unpredictable, costly and unable to produce best-fit software results. Encanvas uniquely automates coding and scripting. Our live wireframing approach means that business analysts can create the apps you need in workshops, working across the desk with users and stakeholders.
When it comes to creating apps to create a data culture and orchestrate your business model, there’s no simpler way to instal and operate your enterprise software platform than AppFabric. Every application you create on AppFabric adds yet more data to your single-version-of-the-truth data insights. That’s because, we’ve designed AppFabric to create awesome enterprise apps that use a common data management substrate, so you can architect and implement an enterprise master data management plan.
Encanvas supplies a private-cloud Customer Data Platform that equips businesses with the means to harvest their customer and commercial data from all sources, cleanse and organize it, and provide tooling to leverage its fullest value in a secure, regulated way. We provide a retrofittable solution that bridges across existing data repositories and cleanses and organizes data to present a useful data source. Then it goes on to make data available 24×7 in a regulated way to authorized internal stakeholders and third parties to ensure adherence to data protection and FCA regulatory standards.
Encanvas Secure and Live (‘Secure&Live’) is a High-Productivity application Platform-as-a-Service. It’s an enterprise applications software platform that equips businesses with the tools they need to design, deploy applications at low cost. It achieves this by removing coding and scripting tasks and the overheads of programming applications. Unlike its rivals, Encanvas Secure&Live is completely codeless (not just Low-Code), so it removes the barriers between IT and the business. Today, you just need to know that it’s the fastest (and safest) way to design, deploy and operate enterprise applications.
Learn more by visiting www.encanvas.com.
Mason Alexander is a senior consultant specializing in helping organizational leadership teams to grow by implementing enterprise software platforms that improve data visibility, process agility; and organizational learning – creating an enterprise that learns and adapts faster. He writes on subjects of change management, organizational design, rapid development applications software, and data science. He can be contacted via his LinkedIn profile.
Article on Top 10 change management software applications.
Wikipedia article on Change Management
Wikipedia article on Situational Applications
Academic paper on Situational Applications